编写服务器
所有的 Netty 服务器都需要以下两个部分:
- 至少一个 ChannelHandler ,该组件实现了服务器对从客户端接收的数据的处理,即它的业务逻辑。
- 引导,这是配置服务器的启动代码。至少,它会将服务器绑定到它要监听的连接请求的端口上。
我们编写一款最简单的应用程序,接收到客户端的消息,并把消息发送给客户端。因为我们的应用程序会响应传入的消息,所以它需要实现 ChannelInboundHandler 接口,用于来定义响应入站(inbound)事件的方法。这个简单的应用程序只需要用到少量的这些方法,所以直接继承 ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter 类也就足够了,它提供了 ChannelInboundHandler 的默认实现。
服务器的 ChannelHandler 组件实现:
// 标示一个 ChannelHandler 可以被多个 Channel 安全地共享
@Sharable
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* 对于每个传入的消息都要调用
*
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf in = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("Server received: " + in.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
// 将接收到的消息写给发送者,而不冲刷出站消息
ctx.write(in);
}
/**
* 通知 ChannelInboundHandler 最后一次对 channelRead() 的调用是当前批量读取中的最后一条消息
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 将未决消息冲刷到远程节点,并关闭该 Channel
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
/**
* 在读取操作期间,有异常抛出时会调用
*
* @param ctx
* @param cause
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
// 打印异常栈跟踪
cause.printStackTrace();
// 关闭该 Channel
ctx.close();
}
}引导服务器的过程涉及:
- 绑定到服务器将在其上监听并接受传入的连接请求的端口。
- 配置 Channel ,以及将有关的入站消息通知给 ChannelHandler 实例。
引导服务器:
public class EchoServer {
private final int port;
public EchoServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws Exception {
final EchoServerHandler serverHandler = new EchoServerHandler();
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
// 指定所使用的 NIO 传输 Channel
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
// 使用指定的端口设置套接字地址
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port))
// 添加一个 EchoServerHandler 到子 Channel 的 ChannelPipeline
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// EchoServerHandler 被标注为 @Sharable,所以我们可以总是使用同样的实例
ch.pipeline().addLast(serverHandler);
}
});
// 异步地绑定服务器,调用 sync() 方法阻塞等待直到绑定完成
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind().sync();
// 获取 Channel 的 CloseFuture,并且阻塞当前线程直到它完成
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 关闭 EventLoopGroup ,释放所有的资源
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new EchoServer(8888).start();
}
}编写客户端
如同服务器,客户端将拥有一个用来处理数据的 ChannelInboundHandler ,在我们这个应用程序场景下,我们可以直接继承 SimpleChannelInboundHander 类即可处理所有需要的任务。
客户端的 ChannelHandler 组件实现:
// 标记该注解的实例可以被多个 Channel 共享
@Sharable
public class EchoClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
/**
* 连接建立
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
// 当被通知 Channel 是活跃的时候,发送一条消息
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Netty rocks!", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
/**
* 每当接收到数据
* TCP保证了字节数组将会按照服务器发送它们的顺序被接收
*
* @param ctx
* @param msg Netty 的字节容器
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception {
// 记录已接收消息的转储
System.out.println("Client received: " + msg.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
// 在发送异常时,记录错误并关闭 Channel
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}引导客户端:
public class EchoClient {
private final String host;
private final int port;
public EchoClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
// 适用于 NIO 传输的 Channel 类型
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
// 设置服务器的 InetSocketAddress
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))
// 在创建 Channel 时(连接被建立时),向 ChannelPipeline 中添加一个 EchoClientHandler 实例
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler());
}
});
// 连接到远程节点,阻塞等待直到连接完成
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect().sync();
// 阻塞,直到 Channel 关闭
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 关闭线程池并且释放所有的资源
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new EchoClient("127.0.0.1", 8888).start();
}
}测试
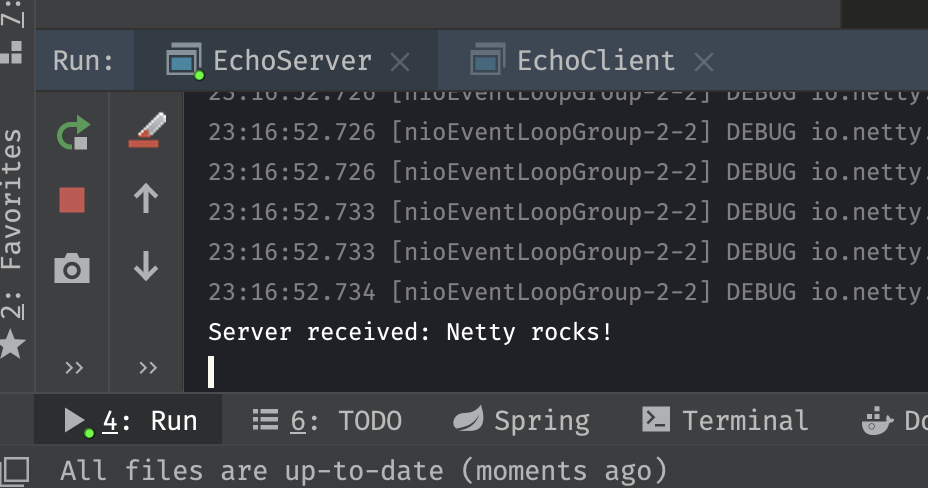
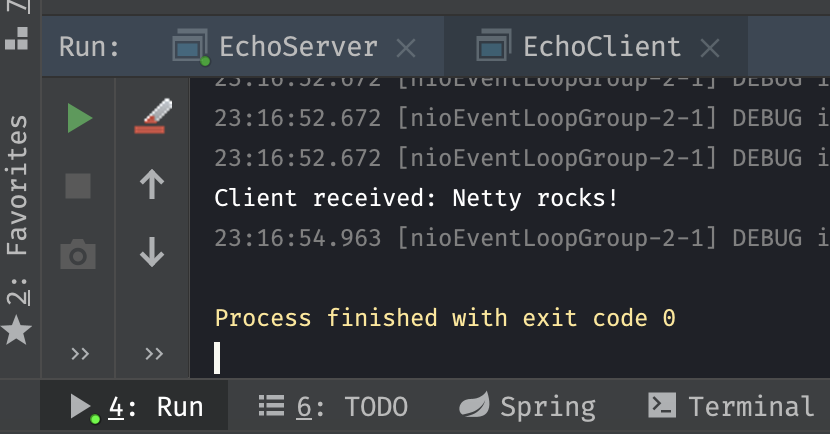
先启动服务器,然后启动客户端。结果服务器接收到客户端发送的信息,打印信息并将信息返回给客户端。客户端接收到服务器返回的信息,打印信息并退出。